Using mines as pumped storage power plants
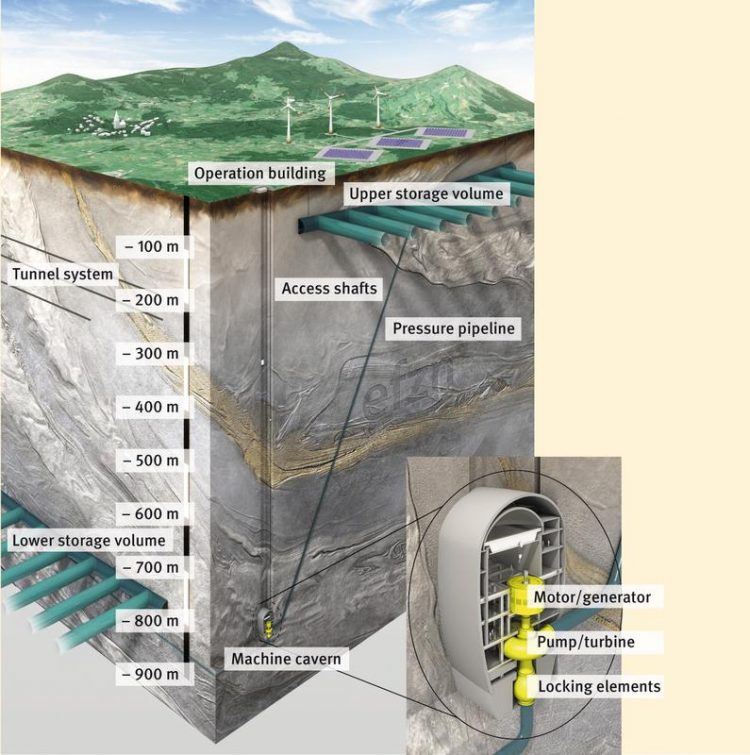
Structure of an underground pumped storage power station. © EFZN
Pumped storage power plants are firmly established in the German power grid: surplus electricity can be stored for a moment and then quickly supplied during a demand peak.
The BINE Projektinfo brochure “Storing wind energy underground” (18/2013) presents a concept of how to reuse abandoned ore mines as pumped storage power plants. This type of underground electricity storage could expand the storage capacity of the power grid considerably. Unlike aboveground power plants, larger landscape interventions would be avoided.
A conventional pumped storage power plant usually consists of two water reservoirs, hydro dams or lakes, between which there is a height difference that is as large as possible. If energy is to be stored, water is pumped from the lower reservoir to the upper one.
When power is required for the grid, water flows back into the lower reservoir, powering a turbine.
This storage principle can also be implemented in former mines. Using the example of the ore mines Grund in the northwestern Upper Harz and Pöhla in the Erzgebirge, the researchers developed a technical and environmental concept. In addition, they compiled reference values of economic efficiency and exploitable potential in Germany.
The comprehensive study was prepared by Energie-Forschungszentrum Niedersachsen and other academic partners from the fields of mining, mechanical engineering and environmental law.
The BINE-projectinfobrochure, which can be obtained free of charge from the BINE Information Service at FIZ Karlsruhe, is available online at www.bine.info or by calling +49 (0)228 92379-0.
Press contact
Uwe Milles
presse(at)bine.info
About BINE Information Service
Energy research for practical applications
The BINE Information Service reports on energy research topics, such as new materials, systems and components, as well as innovative concepts and methods. The knowledge gained is incorporated into the implementation of new technologies in practice, because first-rate information provides a basis for pioneering decisions, whether in the planning of energy-optimised buildings, increasing the efficiency of industrial processes, or integrating renewable energy sources into existing systems.
About FIZ Karlsruhe
FIZ Karlsruhe – Leibniz Institute for Information Infrastructure is a not-for-profit organization with the public mission to make sci-tech information from all over the world publicly available and to provide related services in order to support the national and international transfer of knowledge and the promotion of innovation.
Our business areas:
• STN International – the world’s leading online service for research and patent information in science and technology
• KnowEsis – innovative eScience solutions to support the process of research in all its stages, and throughout all scientific disciplines
• Databases and Information Services – Databases and science portals in mathematics, computer science, crystallography, chemistry, and energy technology
FIZ Karlsruhe is a member of the Leibniz Association (WGL) which consists of 87 German research and infrastructure institutions.
http://www.bine.info/en/press/press-releases/press/pressemitteilung/bergwerke-al… – Download cover, press release and info-pdf
http://www.bine.info/en – BINE Informationsdienst english
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Power and Electrical Engineering
This topic covers issues related to energy generation, conversion, transportation and consumption and how the industry is addressing the challenge of energy efficiency in general.
innovations-report provides in-depth and informative reports and articles on subjects ranging from wind energy, fuel cell technology, solar energy, geothermal energy, petroleum, gas, nuclear engineering, alternative energy and energy efficiency to fusion, hydrogen and superconductor technologies.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



