This special field revolves around processes for modifying material properties (milling, cooling), composition (filtration, distillation) and type (oxidation, hydration).
Valuable information is available on a broad range of technologies including material separation, laser processes, measuring techniques and robot engineering in addition to testing methods and coating and materials analysis processes.

Striking pictures of magnetic waves inside advanced ceramics may be the clue to understanding how they can transmit electricity without losing energy, according to results obtained by two teams of scientists using the UK’s world-leading ISIS neutron source in Oxfordshire and published this week in the journal Nature.
The ceramics, known as high-temperature superconductors, lose all resistance to the flow of electricity when cooled below a critical temperature. Wires made from the ceramics ca

An engineering team at the University of Dundee has just secured funding to work with European colleagues on the construction of artificial corneas which will allow all cornea replacements to go ahead without the patient having to wait for a donor.
The Euro 2.4m project will help people who suffer from a number of diseases requiring corneal grafting including keratoconus – a thinning of the cornea. Instead of relying on donor corneas from an eye bank, the new technology invented by biochemis

The Robosoft company in Bidart (Lapurdi/Labourd) makes and markets robots that are programmed according to the requirements of the customer. These customised devices – robots – carry out numerous tasks that, in general, are laborious for us – lugging heavy loads around, cleaning chores, handling very small objects, and so on. The size and shape of each robot is distinct, according to the task(s) assigned it.
What is manufactured is a robot that is something like a train – it serves as a mean

The main objective of the Dressman robot is to dry and press shirts. On placing a damp shirt on the ironing figure, this dummy inflates with hot air in its interior, and thus puffs the shirt up, removing creases drying the garment (it has to be previously wet and undergone a spin-dry in a washing machine).
The device has a heater box inside with a number of different resistance elements. While we are placing the shirt on it, this box stores up heat in such a way that, when the garment is pos

Microarrays, sometimes called “gene chip” devices, enable researchers to monitor the activities of thousands of genes from a single tissue sample simultaneously, identifying patterns that may be novel indicators of disease status. But generating consistent, verifiable results is difficult because of a lack of standards to validate these analyses, scientists from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and collaborators warn in the May 20 online issue of Clinical Chemistry.
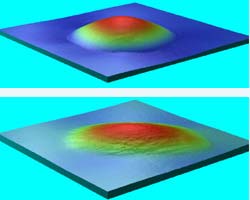
An improved method for correcting nano- and micro-scale friction measurements has been developed by researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). The new technique should help designers produce more durable micro- and nano-devices with moving parts, such as tiny motors, positioning devices or encoders.
Friction measurements made at the micro- and nano-scale can differ substantially due to changes in applied load. In a series of experiments described by nanotribol