This special field revolves around processes for modifying material properties (milling, cooling), composition (filtration, distillation) and type (oxidation, hydration).
Valuable information is available on a broad range of technologies including material separation, laser processes, measuring techniques and robot engineering in addition to testing methods and coating and materials analysis processes.

Experiment uses biomolecules to write on a gold substrate Duke University engineers have demonstrated that enzymes can be used to create nanoscale patterns on a gold surface. Since many enzymes are already commercially available and well characterized, the potential for writing with enzyme “ink” represents an important advance in nanomanufacturing. This research was funded by the National Science Foundation through a Nanotechnology Interdisciplinary Research Initiative (NIRT) grant.

A safer way to heat food products that retains nutritional qualities, which experts acknowledge has a positive effect on health, is being developed with the help of €693,000 from the Food Quality and Safety Programme of the European Union’s Framework Programme
In most cases, the production of safe food products requires some form of heat treatment and, in traditional heating methods, the result is often a loss of nutritional quality. This is because the heat is generated outside the food an
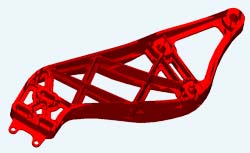
Researchers at Purdue University have developed the first system capable of searching a company’s huge database of three-dimensional parts created with computer-aided design software.
Such “parts search engines” could save time and millions of dollars annually by making it easier for companies to “reuse” previous designs, benefiting from the lessons learned in creating past parts.
“Designers spend about 60 percent of their time searching for the right information, which is rated as

CSIRO marine scientists have developed a technique that gives new hope in the battle to stop the spread of aquatic pests
“What we have is a probe acting as a magnet to detect a needle in a haystack,” says Dr Jawahar Patil, who designed the technique which has been successfully tested in Australia.
The new DNA probe involves seawater sample extraction of DNA, and amplification of a target specific “DNA signature or fingerprint” to identify the presence of pest species in water

Police who need to dust suspicious packages for fingerprints could someday rely on a robotic device to do this dangerous work.
The device, developed by scientists from U of T and the University of Calgary, offers a safe way to collect fingerprint evidence from packages that might be too dangerous for a human to approach. A study describing the development of the device, called a Robot Accessory for Fuming Fingerprint Evidence (RAFFE), appears in the March 2004 issue of the Journal of Forensi

New, biodegradable machining compound is more effective than industry standards
Derived in part from green tea, a new biodegradable machining compound for computer hard drive manufacturing is three to four times more effective than toxic counterparts. In an industry where more than 161 million hard drives leave assembly lines each year, the new compound could significantly improve manufacturing efficiency and minimize environmental risks.
Engineered by John Lombardi of Ve