About 150,000 years ago, an anomalous ice age was triggered by an increasingly salty Mediterranean Sea, a development that’s occurring today and may start new ice sheet growth in the next few decades, according to a study at the University of Minnesota. Robert Johnson, an adjunct professor of geology and geophysics, will present his study of the glaciation 150,000 years ago and discuss its implications for today’s climate on Tuesday, Oct. 29, at the annual meeting of the Geological Society
A team of experts has refuted previous findings published last summer stating that Pfiesteria is not toxic to fish or humans. When they cultured the same strain of P. shumwayae studied by the dissenting scientists, it produced a toxin that killed fish within minutes.
Dr. JoAnn Burkholder, director of North Carolina State University’s Center for Applied Aquatic Ecology, presented the results of the new study Tuesday at the 10th International Conference on Harmful Algae in S
A new giant was born recently in the coastal waters of Antarctica. A series of images captured from May through the beginning of this month by ESA`s Envisat satellite shows the subsequent duel between the new iceberg and another as it breaks free of the Ross Ice Shelf and tries to move north.
Christened C-19 by the US National Ice Centre in Maryland, the new iceberg measured 200 x 32 km, and about 200 m thick.
As seen in the accompanying animation of images acquired by Envi
A U of T study suggests why giant gold and copper deposits are found at some volcanoes but not others, a finding that could point prospectors to large deposits of this and other valuable metals.
“There’s one characteristic that is common to all of these big gold and copper deposits anywhere in the world,” says Professor James Mungall of the Department of Geology. The ocean’s crust that is pushed down under a volcano can start to melt, which it doesn’t normally do. His study, which appea
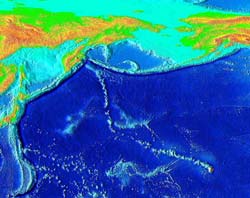
The swirl of malleable rock in the earth’s mantle – located between the earth’s crust and core – may have greater effect on the earth’s surface than was once believed, a Purdue research team reports.
Using computer technology to create three-dimensional models of the earth’s mantle, Purdue’s Scott King has found evidence that some dramatic features of the earth’s surface could be the result of relatively rapid shifts in the direction in which crustal plat

Air-sea interaction tower built off Martha’s vineyard
In the deep waters two miles south of Edgartown on Martha’s Vineyard, not far from where, two centuries ago, the likes of Captain Ahab and a thousand others kept their watch for the great white and his kin, we are now searching to understand another potential beast in those parts: the ocean and the weather.
But this is no allegory. Hoping to avoid any recurrence in these sometimes turbulent waters of the horrendo