
A new discovery by a team of Queen’s University scientists suggests that ancient earth was much colder than previously thought – a discovery that has broad implications for those studying the earth’s climate.
Queen’s researchers have discovered the mineral ikaite in 700-million-year-old marine sedimentary rocks in the Mackenzie Mountains of the Northwest Territories and eastern Yukon. This discovery proves that the ancient ocean was much colder than previously believed, says Noel Ja
The combined Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory/University of Rhode Island coupled hurricane-ocean model has helped to improve intensity predictions during tropical storms. However, scientists have found that the model consistently under-predicts maximum wind speed in very strong hurricanes.
In the current issue of the Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, University of Rhode Island physical oceanographer Dr. Isaac Ginis describes how he and a team of scientists are refining the
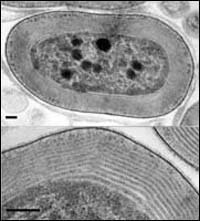
Salton Sea find shares ’gene-jumping’ history with its oceanic relatives
Scientists at the University of Oregon have discovered a form of blue-green algae that lives independently in California’s Salton Sea, using near-infrared light for photosynthesis, according to an article published in this week’s online edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
“This new strain of Acaryochloris is unique because it is able to live on its own,” says UO
Scientists using NASA satellite data found the shape of the Earth appears to be influenced by big climate events that cause changes in the mass of water stored in oceans, continents and atmosphere.
The study’s principal researchers are Minkang Cheng and Byron D. Tapley, of the Center for Space Research, University of Texas at Austin. They reviewed climate events like El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) and Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO) that affect the amount of water moving in
The depth in the ocean where calcium carbonate dissolves at a faster rate than it is deposited is called the calcite compensation depth (CCD). At present this depth is approximately 4,500 meters (14,700 feet) with some variation between and within ocean basins. Because the CCD is linked to ocean acidity, which is, in turn, linked to atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations and, hence, to global climate, it is important for scientists to understand the impact of possible changes in its depth.
The position of the earth’s tectonic plates is key, says Lehigh University seismologist
The location of the recent earthquake that triggered a deadly tsunami in the Indian Ocean came as no surprise to geologists, says Anne Meltzer, a world-renowned seismologist at Lehigh University. “Earthquakes like this one happen only once every 50 to 100 years and they happen in very specific locations,” says Meltzer, who has supervised two major international seismology research project