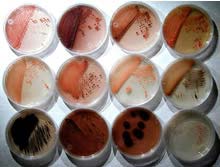
Promising cancer-fighting candidates emerge from tropical ocean ‘mud’
Although the oceans cover 70 percent of the planet’s surface, much of their biomedical potential has gone largely unexplored. Until now.
A group of researchers at Scripps Institution of Oceanography at the University of California, San Diego, have for the first time shown that sediments in the deep ocean are a significant biomedical resource for microbes that produce antibiotic molecules.
In a seri
Findings detailed in Jan. 16 issue of Nature; greenhouse gases implicated
A study by University of Massachusetts Amherst geoscientist Robert DeConto posits an alternative theory regarding why Antarctica suddenly became glaciated 34 million years ago. The study challenges previous thinking about why the ice sheet formed and holds ramifications for the next several hundred years as greenhouse gases continue to rise. DeConto, who collaborated with David Pollard of Pennsylvania State Univ
Climate change had little to do with the demise of the dinosaurs, but the last million years before their extinction had a complex pattern of warming and cooling events that are important to our understanding of the end of their reign, according to geologists.
“The terrestrial paleoclimate record near the K-T is historically contradictory and poorly resolved,” says Dr. Peter Wilf, assistant professor of geosciences at Penn State. “In contrast, the resolution of K-T marine climates that has
Local fisheries part of bigger cycle affecting entire Pacific Ocean
In the late 1930’s, California’s sardines supported the biggest fishery in the western hemisphere, with more than half a million tons of fish caught each year. By the mid-1950s, the sardines had virtually disappeared. Although fishing pressure may have played a part in this process, new research published in the current issue of Science indicates that the sardines’ demise was part of a 50-year cycle tha
Using a state-of-the-art computer model of the lunar interior, geophysicists at the University of California, Berkeley, have shown that a mighty burp early in the moon’s history could account for some of its geologic mysteries.
The burp of hot rock, like a blob rising to the top of a lava lamp, would have lifted a blanket covering the moon’s core, allowing the core to cool quickly enough to produce a magnetic field.
The moon has long since cooled off and the global magne
Unless the pace of global warming is abated, polar bears could disappear within 100 years, says a University of Alberta expert in Arctic ecosystems.
While it has been known for some time that the polar bear is in trouble, new research shows that Arctic ice–the polar bear’s primary habitat–is melting much faster than scientists had believed, says U of A biologist Dr. Andrew Derocher.
“The climate predictions coming out are showing massive changes in sea-ice distribution,” sa