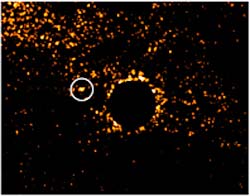
Astronomers are announcing today the first results of a search for extrasolar planets and brown dwarfs in an unlikely place–the stellar graveyard. The report, titled “Searching for Extrasolar Planets in the Stellar Graveyard,” is being presented at the American Astronomical Society meeting in San Diego, California, by John Debes, a graduate student at Penn State; Steinn Sigurdsson, associate professor of astronomy and astrophysics at Penn State University; Bruce Woodgate, of the NASA Goddard Spa
Finding how the fowl-borne bacteria Campylobacter jejuni makes at least a million Americans miserable for a week each year is on the plates of two Medical College of Georgia microbiologists.
Raw and undercooked poultry and meat, raw milk and untreated water are sources for Campylobacter, the most common bacterial cause of diarrhea in the United States, according the U.S. Public Health Service.
But finding how these bacteria that happily co-exist with chickens and turkeys

Carbon and silicate grains in interplanetary dust particles are helping scientists solve a 40-year-old astronomical mystery.
Using a transmission electron microscope, researchers from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory have detected a 5.7-electron volt or 2175 Å (angstrom) wavelength feature in interstellar grains that were embedded within interplanetary dust particles (IDPs). They found that this feature is carried by carbon and amorphous silicate grains that are abundant in

More than 250 new examples of England’s finest array of prehistoric rock art carvings, sited close to the Scottish border, have been discovered by archaeologists compiling a unique database.
Now over one thousand of the ’cup and ring’ carvings can be admired on a new website, which carries 6,000 images and is said to be the most comprehensive of its kind in the world. The site, which goes live today, includes the 250 panels unearthed during a two-and-a-half year t
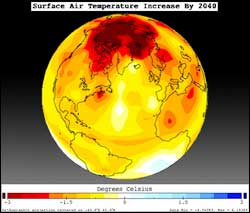
College and high school students can now see how Earth’s climate is changing without leaving their computers.
NASA and other organizations use NASA’s global climate computer model (GCM) to see how Earth’s climate is changing. A GCM calculates many things, such as how much sunlight is reflected and absorbed by Earth’s atmosphere, the temperature of the air and oceans, the distribution of clouds, rainfall, and snow, and what may happen to the polar ice caps in th
It is now significantly easier to search long stretches of DNA for genetic changes associated with disease, thanks to scientists at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis.
The researchers developed a method called direct genomic selection that accelerates the transition between family or population-based studies of disease inheritance patterns and identification of genetic variations that may contribute to disease. That transition normally slows down dramatically wh