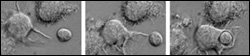
The dendritic cells act as the body’s sentries, standing guard around the clock. As soon as they detect a potential enemy, they alert the T cells, whose role is to defend the body.
At the Institut Curie, CNRS researchers in an Inserm laboratory have filmed the encounter of dendritic cells and T cells. They have shown that this “rendez-vous”, which is indispensable for the activation of the immune system, cannot take place in the absence of the proteins Rac 1 and 2. Published in the
C. elegans model helps identify protein linked to long QT syndrome – Could help lead to development of drugs that don’t cause calcium channel block
The worm C. elegans seems an unlikely candidate for studies related to cardiac arrhythmias. After all, the microscopic organism doesn’t even have a heart.
That fact did not deter Christina I. Petersen, Ph.D., research assistant professor of Anesthesiology at Vanderbilt University Medical Center. Petersen and colleagues, includ
Sophisticated tools used to survey and monitor passenger flows through busy metro stations may result in unmanageable data loads. ADVISOR’s decision support tools reduce the workload of operators and increase the utility of the data output.
ADVISOR, which stands for Annotated Digital Video for Intelligent Surveillance and Optimised Retrieval, “is a significant aid to the operators in charge of metro security,” says project coordinator Michael Naylor. “The principal of the [ADVISO
A type of ‘friendly bacteria’ has been the key for researchers at the University of Dundee who have just developed a treatment that offers the opportunity of new therapies for the management of one of the UK’s most common forms of inflammatory bowel disease – ulcerative colitis. Results from a four-week patient trial led by Professor George Macfarlane showed that many of the patients’ symptoms were dramatically reduced to near normal levels.
Affecting an estimated fifty thous
A Mayo Clinic researcher is the first to develop a series of three-dimensional (3D) models of an enzyme responsible for the replication of the deadly SARS (Severe Acute Respiratory syndrome) virus. These instantaneous “structures-in-time” are central to designing an anti-SARS drug — and are therefore a welcome advance as the virus continues to threaten public health.
The structure and dynamics of the SARS viral enzyme, called chymotrypsin-like cysteine proteinase, is described in
Certain rare gene mutations can contribute significantly to low levels of a beneficial form of cholesterol in the blood, researchers have found. Low levels of this cholesterol, known as high-density lipoprotein (HDL), are a major risk factor for heart disease.
Gene mutations previously known to affect HDL levels had small effects individually, and it was thought many such mutations needed to accumulate before HDL levels were significantly reduced. The new finding, however, demonst