Cornell University microbiologists, looking for bioremediation microbes to “eat” toxic pollutants, report the first field test of a technique called stable isotopic probing (SIP) in a contaminated site. And they announce the discovery and isolation of a bacterium that biodegrades naphthalene in coal tar contamination.
Although naphthalene is not the most toxic component in coal tar, the microbiologists say their discovery might eventually help to speed the cleanup of hundreds of 19th and 20
How can you be sure your on-line transactions are secure, and find out if anybody has been siphoning off money from your credit card? The European Commission’s Joint Research Centre (JRC) has developed a way of handling electronic information to protect the rights of cyberspace users and guard against fraud when buying on the Internet.
The EU Cyber Tools On-Line Search for Evidence (CTOSE) project helps identify, secure, integrate and present electronic evidence on on-line criminal offence
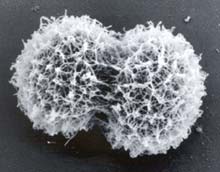
An asteroid that has eluded astronomers for decades turns out to be an unusual pair of objects traveling together in space, a UCLA planetary scientist and colleagues report.
The asteroid Hermes was rediscovered last week after being lost for 66 years. Now Jean-Luc Margot, a researcher in UCLA’s department of Earth and space sciences, has determined that the asteroid is, in fact, two objects orbiting each other. The two objects together would cover an area approximately the size

An estimated 5,000 previously unknown ocean fish species and hundreds of thousands of other marine life forms are yet to be discovered, according to scientists engaged in a massive global scientific collaboration to identify and catalog life in the oceans.
The new marine fish species, being identified at an average rate of 160 per year (roughly three new species per week since year 2000), are being catalogued and mapped by the Census of Marine Life (CoML), an unprecedented cooperativ
The signal, called Hedgehog, tells cells when and where to grow during embryonic development and is turned on in primitive cells,
For more than a century, biologists have been working to assign plants, animals and microbes their respective places on the tree of life. More recently, by comparing DNA sequences from a few genes per species, scientists have been trying to construct a grand tree of life that accurately portrays the course of life on Earth, and shows how all organisms are related, one to another.
However, despite the detailed insights provided by individual genes, that approach has proved cumbersome in its