
In search of cosmic mayhem
A physicist at Washington University in St. Louis working with scientists at the Smithsonian Institution is unveiling the dark, violent side of the universe.
Studying the highest energy photons known to science, Washington University Associate Professor of Physics James H. Buckley, Ph.D., and his colleagues are analyzing bursts of gamma rays released from massive black holes at the center of so-called active galaxies.
Using the Whipple Ob
Two of the three largest impact craters on Earth have nearly the same size and structure, researchers say, but one was caused by a comet while the other was caused by an asteroid. These surprising results could have implications for where scientists might look for evidence of primitive life on Mars.
Susan Kieffer of the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Kevin Pope of Geo Eco Arc Research and Doreen Ames of Natural Resources Canada analyzed the structure and stratigraphy of the 65 m
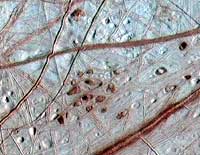
The oozing of glacial material in the floating ice shell on Jupiter’s moon Europa has important implications for future exploration of the enigmatic moon and prospects of life in its ice-covered ocean, according to a University of Colorado at Boulder professor.
Robert Pappalardo, an assistant professor in the astrophysical and planetary sciences department and one of the world’s foremost Europa experts, said the icy moon is believed to contain an ocean some 13 miles under its icy
A high-throughput assay developed by University of Illinois at Chicago chemists has led to discovery of a small organic compound that shows the unusual ability to inhibit cell migration. The new compound, identified as UIC-1005, may play a role in developing new kinds of cancer drugs.
The findings are published in the November issue of the journal ChemBioChem.
“We’ve been looking for chemical compounds that slow the process of cell migration,” said Gabriel Fenteany, assistant
UCLA Neuropsychiatric Institute researchers have localized a region on chromosome 16 that is likely to contain a risk gene for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, the most prevalent childhood-onset psychiatric disorder.
Their research, published in the October edition of the American Journal of Human Genetics, suggests that the suspected risk gene may contribute as much as 30 percent of the underlying genetic cause of ADHD and may also be involved in a separate childhood onset disorder

Astronomers have identified the vivid scar of a cosmic catastrophe: a blue arc thousands of light years long produced when a galaxy pulled in a smaller satellite galaxy and tore it apart.
The streak is composed of clusters of young blue stars that formed as the larger galaxy, Centaurus A, absorbed the smaller galaxy about 200 million to 400 million years ago. Researchers will report in the December Astronomical Journal that their discovery suggests absorption of smaller galaxies may be a sig