DNA of Xenopus tropicalis will provide new clues to vertebrate development
In their continuing search for new clues to how human genes function and how vertebrates develop and evolve, researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Joint Genome Institute (JGI) are gearing up to map the DNA of a diminutive, fast-growing African frog named Xenopus tropicalis .
Frogs have long been a favorite subject for biologists because their growth from eggs to tadpoles to

A sort of biochemical scaffold for a compound that enables blood pressure to be low, heart bypass grafts to remain open and nerves to communicate has been identified by Medical College of Georgia researchers.
Researchers say identifying the framework for how these and other very positive health benefits occur should help them find ways to augment the benefits and identify new treatments for cardiovascular disease, which may result when the support structure falls apart.
“It’s
Researchers from the University of Chicago have identified a gene defect that causes the development of leukemia in children with Down syndrome. The discovery, scheduled for Advance Online Publication on Nature Genetics’s website on 12 August, could speed diagnosis and provide a new target for therapy.
Children with Down syndrome are 10 to 20 times as likely as unaffected children to develop leukemia. They most commonly develop a type known as acute megakaryoblastic leukemia (AMKL), wh

Rich and Inspiring Experience with NGC 300 Images from the ESO Science Data Archive
A series of wide-field images centred on the nearby spiral galaxy NGC 300, obtained with the Wide-Field Imager (WFI) on the MPG/ESO 2.2-m telescope at the La Silla Observatory, have been combined into a magnificent colour photo.
These images have been used by different groups of astronomers for various kinds of scientific investigations, ranging from individual stars and nebulae in NGC 300, to distant gal
A gene thought to keep a single X chromosome turned on in mice plays no such role in humans, Johns Hopkins researchers report in the August issue of the American Journal of Human Genetics.
The finding is likely to relegate the disproven gene to relative obscurity, at least in humans, says Barbara Migeon, M.D., of the McKusick-Nathans Institute of Genetic Medicine, whose laboratory found the human version of the gene in 2001. It also moves the search for the gene from the X chromosome to the
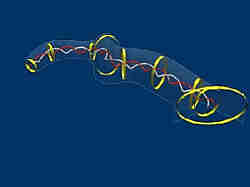
Researchers at Case Western Reserve University have discovered kinks in aggrecan, a widely studied protein at the submolecular root of arthritis, a finding that brings scientists closer toward new drugs and other interventions to prevent or alleviate the disease. “Aggrecan acts to organize and densely pack sugar molecules that give cartilage its resilience,” said Steven Eppell, an assistant professor of biomedical engineering and director of the Nanoscale Orthopedic Biomaterials Labo