Iron is vital for cells, because it catalyzes key enzyme reactions; it is also crucial for respiration, fixing atmospheric oxygen to hemoglobin in red blood cells. Iron deficiency can lead to severe anemia, with inadequate tissue oxygenation. An excess of iron is also toxic, as it facilitates the generation of free radicals that can attack the liver, heart and pancreas. This is the case in hereditary hemochromatosis, a genetic disorder which, in 80% of cases, is linked to a point mutation in the Hfe-
Whether it will compete for the title of a girl’s best friend remains to be seen but the element osmium can already challenge diamond in at least one respect: stiffness. According to a report published in the current issue of Physical Review Letters, osmium can withstand compression better than any known material. The results provide a potentially new lead in the search for superhard materials.
Diamond’s ability to resist scratches, dents and chipping–in short, its hardness–makes
The first clinical trial in Europe of a revolutionary approach to diagnosing breast cancer has just got under way at one of the UK’s leading breast cancer centres.
The research involves a minute endoscope, no thicker than a few strands of human hair, which can pass through the nipple and search for the earliest signs of cancer within the breast.
Consultant breast surgeon, Dr Nicolas Beechey-Newman from Guy’s Hospital in London, told a news briefing at the 3rd European Breast Cancer Confe
New algorithm exploits community structure of the web.
The web has spontaneously organized itself into communities. A new search algorithm that pinpoints these could help surfers find what they want and avoid offensive content.
Page builders can link anywhere. But they don’t, Gary Flake, of the NEC Research Institute in Princeton, and his colleagues have found. Instead, pages congregate into social groups that focus most of their attention on each other.
Web dir
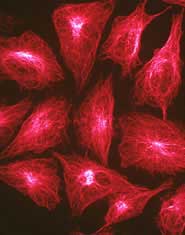
Glowing nanobots map microscopic surfaces.
Unleashing hordes of molecular robots to explore a surface’s terrain can produce maps of microscopic structures and devices with higher resolutions than those produced by conventional microscopes, new research shows.
Each robot has a ’light’ attached to it, allowing its random movements to be tracked around obstacles, through cracks or under overhangs. Adding the paths of hundreds of wandering nanobots together builds up a map of th

Markus Landgraf of the European Space Agency and colleagues (*) have found the first direct evidence that a bright disc of dust surrounds our Solar System, starting beyond the orbit of Saturn.
Remarkably, their discovery gives astronomers a way to determine which other stars in the Galaxy are most likely to harbour planets and allows mission planners to draw up a ’short-list’ of stars to be observed by ESA’s future planet-search missions, Eddington and Darwin.
The discovery of th