
Findings show similarities to and differences from cuprate superconductors, including more complex electronic structure. Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory have discovered new details about the electrons in a nickel-based family of superconducting materials. The research, described in two papers published in Physical Review X, reveals that these nickel-based materials have certain similarities with—and key differences from—copper-based superconductors. Comparing the two kinds of “high-temperature” superconductors may help scientists zero in on key features essential for these…
Results point to importance of internal structure of nucleons—and need for new measurements to disentangle other contributions. New measurements of how particles flow from collisions of different types of particles at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC) have provided new insights into the origin of the shape of hot specks of matter generated in these collisions. The results may lead to a deeper understanding of the properties and dynamics of this form of matter, known as a quark-gluon plasma (QGP). QGP is…

The term aptamer means something like “fitting pieces” (from the Latin word aptus, meaning to fit, and the Greek word meros, meaning piece). Aptamers consist…

It is the breakthrough that physicists and chemists around the world have long anticipated and it will play a pivotal role in information technology in coming…

The Joint Science Conference (GWK) of the federal and state governments has ratified the 2015 Academies’ Program, coordinated by the Union of the German…
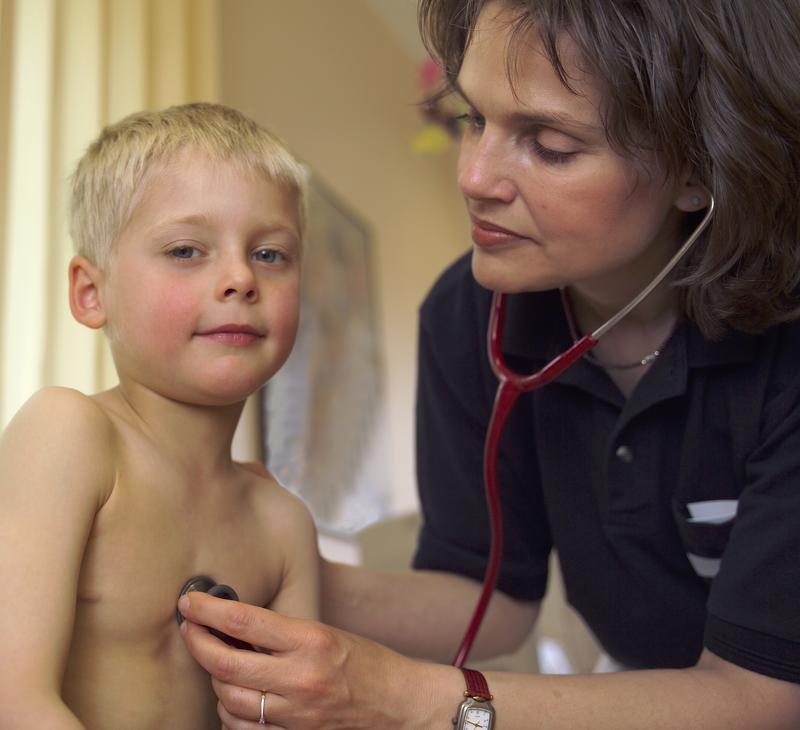
If pathogenic agents penetrate our body, our immune system is put on high alert. The body reacts with inflammatory processes, initiating a whole series of…
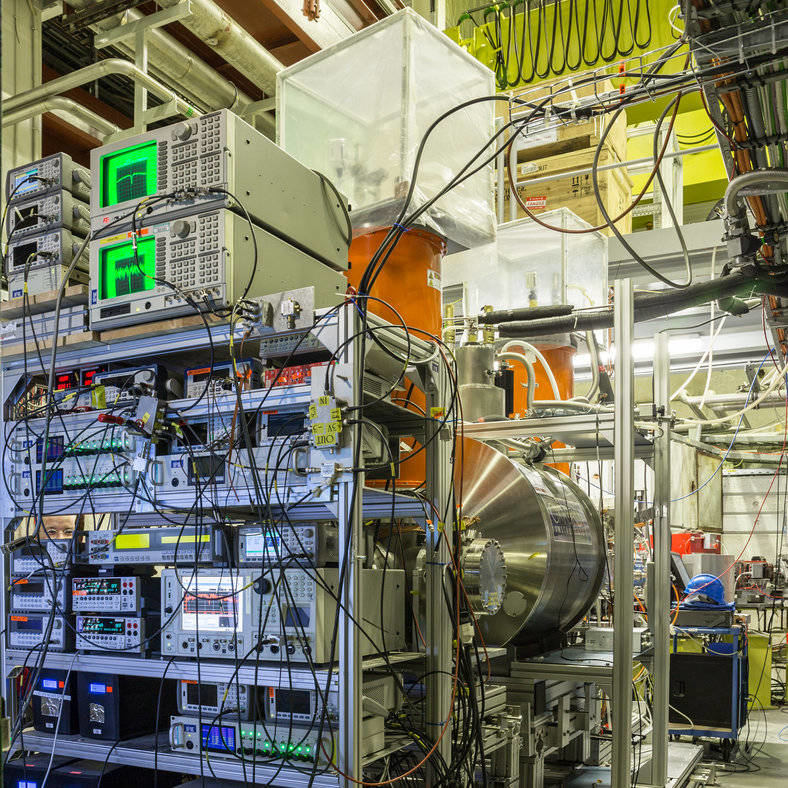
As self-evident as it is that matter exists, its origins are just as mysterious. According to the principles of particle physics, when the universe was…

The total uptake of carbon dioxide by ecosystems via photosynthesis is the largest flux in the global carbon cycle. The intensity of this “natural CO₂ pump”…
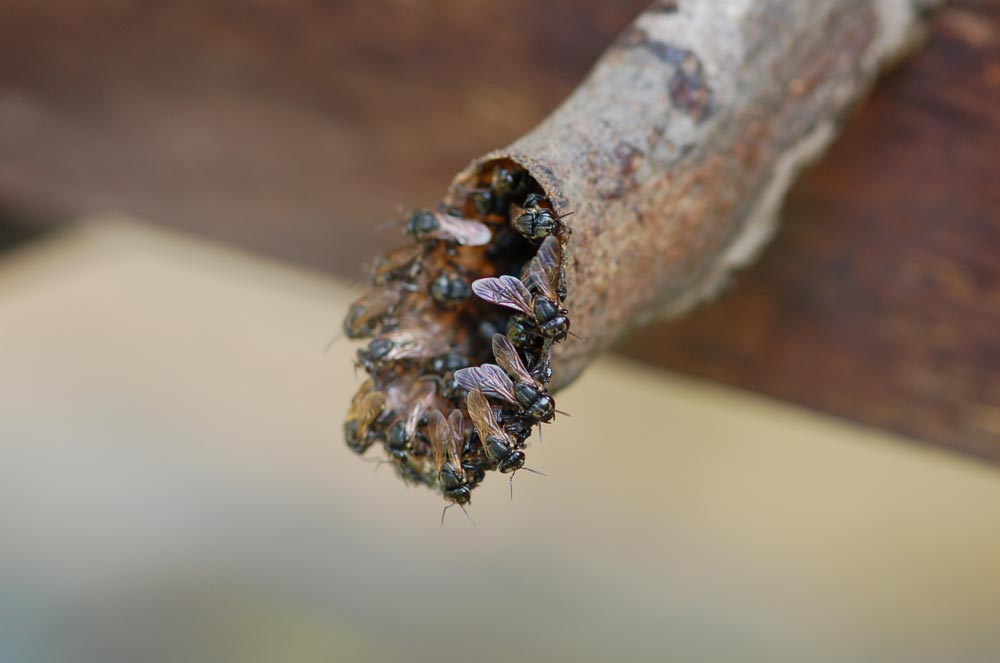

Although stingless bees do not have a sting to fend off enemies, they are nonetheless able to defend their hives against attacks. Only four years ago it was…
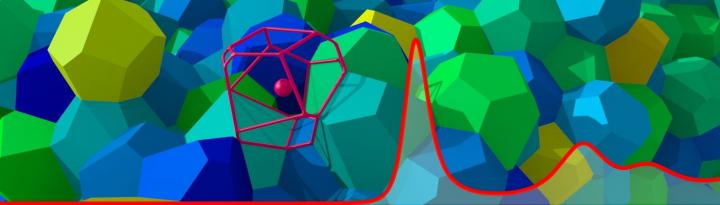
Partitioning space into cells with optimum geometrical properties is a central challenge in many fields of science and technology. Researchers of Karlsruhe…

Analysis of lightweight nuclei emerging from gold ion collisions offers insight into primordial matter phase changes. Physicists analyzing data from gold ion smashups at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC), a U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science user facility for nuclear physics research at DOE’s Brookhaven National Laboratory, are searching for evidence that nails down a so-called critical point in the way nuclear matter changes from one phase to another. New findings from members of RHIC’s STAR Collaboration published in Physical…

New measuring node was placed off Boknis Eck today. One of the oldest marine time series stations in the world is located in Eckernförde Bay, just under two kilometres off the coast: Boknis Eck. Since 1957, data on the state of the Baltic Sea have been collected regularly from a ship and, since 2016, also from an underwater observatory on the seafloor. After the device disappeared in 2019, the GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel today launched a new,…

For decades, the problem of increasing and persistent European unemployment has been at the center of attention of European academics, policy makers, and the…

A team led by Prof Dmitry Budker has continued their search for dark matter within the framework of the ‘Cosmic Axion Spin Precession Experiment’ (or ‘CASPEr’…
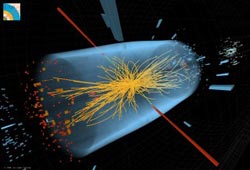
It describes the latest results from two experiments at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at CERN that are searching for signs of the Higgs boson, a subatomic…
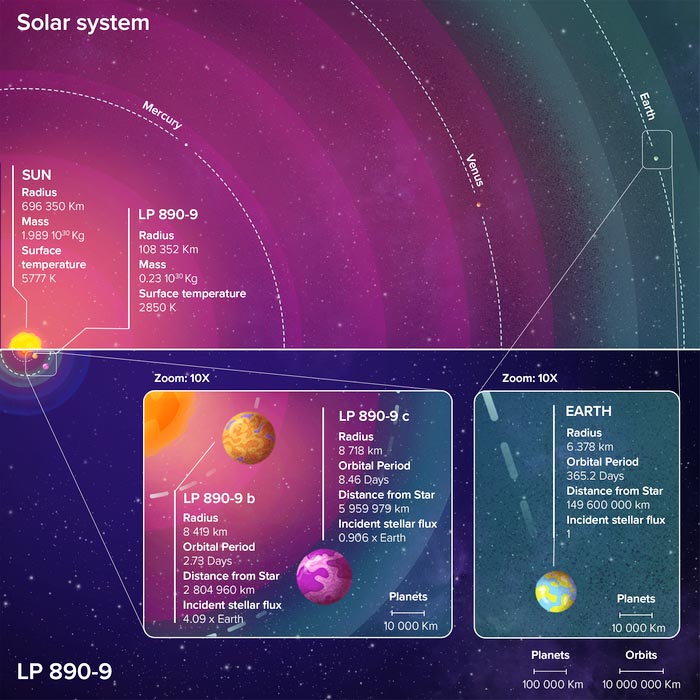
An international team of scientists, led by Laetitia Delrez, astrophysicist at the University of Liège (Belgium), has just announced the discovery of two ‘super-Earth’ type planets orbiting LP 890-9. Also known as TOI-4306 or SPECULOOS-2, this small, cool star located about 100 light-years from our Earth is the second coolest star around which planets have been detected, after the famous TRAPPIST-1. This important discovery is published in the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics. A first planet, LP 890-9b (or TOI-4306b), the…

Almost half of the first top 10 websites displayed by leading search engines on vaccination are emotive “anti” sites, finds a study in the Archives of Disease in Childhood. Many masquerade as official scientific sites, making it easier for users to be misinformed, say the authors.
The researchers keyed in the terms “vaccination” and “immunis(z)ation” into seven leading search engines: Google; Netscape; Altavista; GoTo; HotBot; Lycos; and Yahoo. They then used just the term “vaccination,” for

UC Berkeley scientist urges drilling into frozen lake under ice near South Pole as prelude to drilling into subglacial lakes in Antarctica and into Mars polar caps
Measurements of the ice temperature far below the South Pole suggest that a so-called “lake” discovered at the base of the ice is most likely permafrost – a frozen mixture of dirt and ice – because the temperature is too low for liquid water.
Far from being a disappointment, says a University of California, Berkeley p

Speed-up may make “topic-sensitive” page rankings feasible Computer science researchers at Stanford University have developed several new techniques that together may make it possible to calculate Web page rankings as used in the Google search engine up to five times faster. The speed-ups to Google’s method may make it realistic to calculate page rankings personalized for an individual’s interests or customized to a particular topic. The Stanford team includes grad

Astronomers looking for planetary systems that resemble our own solar system have found the most similar formation so far. British astronomers, working with Australian and American colleagues, have discovered a planet like Jupiter in orbit round a nearby star that is very like our own Sun. Among the hundred found so far, this system is the one most similar to our Solar System. The planet’’s orbit is like that of Jupiter in our own Solar System, especially as it is nearly circular and there