
The Second Assessment of Climate Change for the Baltic Sea Basin (BACC II), a recently published report, serves as a revision and expansion of the 2008 edition…
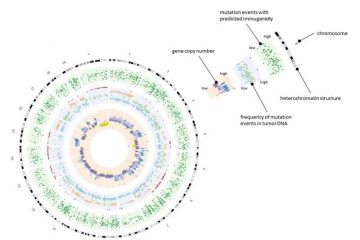
Mainz-based researchers have made significant advances with regard to the development of individualized immunotherapy strategies for treating cancer. They have…
In general, injured peripheral nervous tissue possesses the capacity to regenerate severed axons and therefore the ability for repair. Mechanisms of so-called neuroregeneration may include generation of new glia, extension of axons, re-myelination or restoration of functional synapses. However, the ability for neuroregeneration differs strongly between the peripheral nervous system (PNS) and the central nervous system (CNS). However, although injured axons of the peripheral nervous system show generally greater potential for intrinsic axonal regrowth, functional regeneration is often limited, mainly due to a decline in neurotrophic support from Schwann cells over time and axonal misguidance.
These aspects become particularly evident in cases of long distance regeneration, for example after sciatic nerve injury in legs or median nerve damage in arms. Therefore, the development of novel therapeutic measures aiming to accelerate axon regenera-tion and thereby improving functional recovery is highly desirable. It was found by the inventors of the present invention that the natural product parthenolide and its derivatives facilitate the axonal growth and guidance of injured peripheral nerves in cell culture and most significantly also in vivo. The inventors demonstrate that the intraneural injection of parthenolide at the regenerating nerve results in an improved functional motor recovery as well as in an improved sensory functional recovery.
The analysis of the mRNA content of a cell or a tissue via sequencing provides a method for functional analysis. In common protocols, prior to the sequencing procedure itself the mRNA has to be reverse transcribed into cDNA, followed by random shearing into cDNA fragments, linker ligation, and amplification via PCR. The library of PCR amplicons can then be sequenced by various methods of next generation sequencing (NGS). In many protocols, the primers used for the reverse transcription (RT) or ligation have to be removed before sequencing. Typically, this is achieved by performing a polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, which suffers from poor quantitative yield and poor discrimination between molecules of similar size. Additionally, PCR amplification can lead to biased quantification of rare mRNA species. The present invention allows overcoming these problems by using a new protocol, which consists of the following steps:
1) RT of mRNA into cDNA in presence of dUTP
2) RNA digestion and 3’ end blocking of RT primer with ddTTP
3) Enzymatic cleavage at positions of dUTP incorporation
4) cDNA circularization
5) NGS
In «Nature Nanotechnology», the researchers describe a novel experimental setup with which the tiny magnetic fields of the nuclear spins of single biomolecules…

After more than 20 years of research, scientists of the Experimental and Clinical Research Center (ECRC), a joint cooperation between the Max Delbrück Center…