Planning for a growing elderly population

By 2050, the world’s population aged 60 years and older is expected to reach 2 billion, of which 80% will live in low- and middle-income countries.
We know that not all people age the same way, as how healthy older people are very much depends on their physical and social environments, the health and social support systems in their countries, as well as on their personal characteristics.
The effect is that some 80 year-olds may have physical and mental capacities similar to many 30 year-olds, while others may experience significant declines in their physical and mental health, even at a much younger age.
Policymakers need comprehensive information around how people are aging in their countries and how much support they would need when they start to experience physical limitations related to old age, to enable them to plan for future public health infrastructure and services to provide for older people’s needs.
While European countries and the US have been conducting extensive surveys on aging and health for many years, there is very limited national information available for low- and middle-income countries.
According to the authors of the new study published in Scientific Reports, only a few studies focus on low-income countries, and even fewer use comparable health measures.
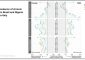
Using data from the World Health Survey and the UN World Population Prospects, the study for the first time makes projections of older adults with severe activity limitations for low- and middle-income countries.
“Just like high-income countries, low- and middle-income countries face a continuous increase in their share of older adults. Up to now, we however did not know much about how people age in these countries. In this study, we wanted to answer questions like whether we should expect many unhealthy older adults.
How do people in low- and middle-income countries age? And, how many older adults with severe activity limitations, that most likely will not be able to live an independent life, can we expect in the next 30 years?” explains Daniela Weber, lead author of the study and a researcher in the IIASA World Population Program.
Applying an innovative methodology developed at IIASA, the researchers specifically looked at health status based on the activity limitations of older adults across the world and forecasted the share of men and women over the age of 50 with severe activity limitations in 23 low- and middle-income countries.
The results revealed constant prevalence rates of older adults with severe activity limitations in low- and middle-income countries for the next 30 years, but overall, the authors say that they were surprised to observe similar health trends in these countries than in high-income countries. In addition, the study’s projections show large variation in the proportion of older adults with physical limitations across the 23 countries investigated.
This can be attributed to disparities in health conditions in the respective countries, but also to differences in cultural peculiarities of reporting (such as it being more common to complain in some cultures than in others), and historical perceptions of health. With that said, all 23 countries are facing considerable demographic changes that will require policy interventions.
“The significance of population aging and its global implications cannot be overstated. It is important to raise awareness, not only about global issues pertaining to population aging, but also the importance of rigorous cross-national research and policy dialogue that will help address the challenges and opportunities of an aging world.
This study contributes to the body of research that will help policymakers prepare for a future marked by the challenges associated with the continued growth of the world’s aging population. Preparing financially for longer lives and finding ways to reduce aging-related disability are likely to become national and global priorities,” concludes study author and IIASA researcher, Sergei Scherbov.
Reference
Weber D & Scherbov S (2020). Prospects of activity limitations among older adults in 23 low- and middle-income countries. Scientific Reports DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-67166-4
Contacts:
Researcher contact
Daniela Weber
Research Scholar
IIASA World Population Program
Tel: +43 2236 807 232
weberd@iiasa.ac.at
Sergei Scherbov
Research Scholar
IIASA World Population Program
Tel: +43 2236 807 584
scherbov@iiasa.ac.at
Press Officer
Ansa Heyl
IIASA Press Office
Tel: +43 2236 807 574
Mob: +43 676 83 807 574
heyl@iiasa.ac.at
About IIASA:
The International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis (IIASA) is an international scientific institute that conducts research into the critical issues of global environmental, economic, technological, and social change that we face in the twenty-first century. Our findings provide valuable options to policymakers to shape the future of our changing world. IIASA is independent and funded by prestigious research funding agencies in Africa, the Americas, Asia, and Europe. www.iiasa.ac.at
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Social Sciences
This area deals with the latest developments in the field of empirical and theoretical research as it relates to the structure and function of institutes and systems, their social interdependence and how such systems interact with individual behavior processes.
innovations-report offers informative reports and articles related to the social sciences field including demographic developments, family and career issues, geriatric research, conflict research, generational studies and criminology research.
Newest articles

Witness Groundbreaking Research on Achilles Tendon Recovery
Achilles tendon injuries are common but challenging to monitor during recovery due to the limitations of current imaging techniques. Researchers, led by Associate Professor Zeng Nan from the International Graduate…

Why Prevention Is Better Than Cure—A Novel Approach to Infectious Disease Outbreaks
Researchers have come up with a new way to identify more infectious variants of viruses or bacteria that start spreading in humans – including those causing flu, COVID, whooping cough…

Durable, Efficient, Sustainable: The Rise of Cerium Oxide Thermal Switches
Groundbreaking cerium oxide-based thermal switches achieve remarkable performance, transforming heat flow control with sustainable and efficient technology. Cerium Oxide-Based Thermal Switches Revolutionize Heat Flow Control Thermal switches, which electrically control…