Learning by doing
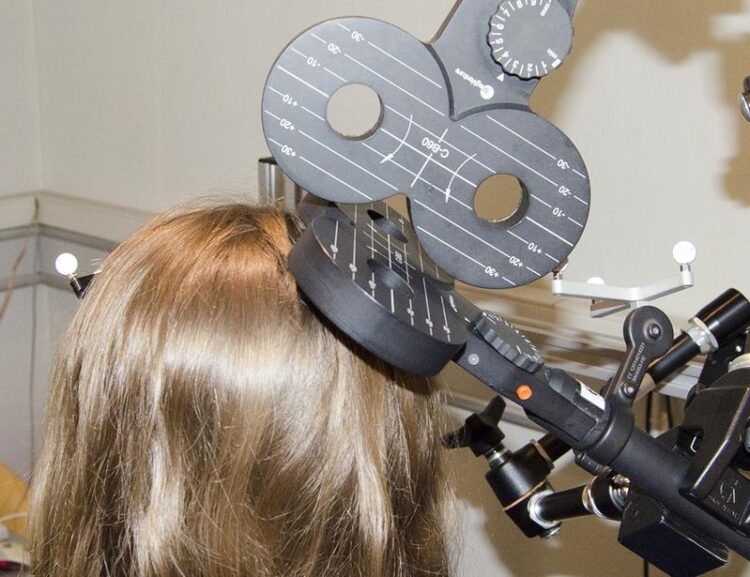
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a neuroscience technique in which specific brain areas can be stimulated by magnetic pulses.
Copyright: Chair of Cognitive and Clinical Neuroscience/TUD
How the brain’s motor system can support vocabulary learning.
The motor cortex is a brain region known to control the body’s voluntary movements. However, the team of neuroscientists have now shown that it can also help translating foreign language words into one’s native language. Their study has been published recently in the renowned Journal of Neuroscience.
The study
Participants in the study learned foreign language words by performing semantically-related gestures over four days of training. After the training, the participants heard the words that they had learned and were asked to translate them into their native language. A neuroscience technique known as transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), in which magnetic pulses stimulate specific brain areas, was used to interfere with processing in the motor cortex during the translation task. The scientists found that this interference slowed down the translation of words learned with gestures. This slowing was not observed in response to the control TMS, which does not interfere with motor cortex processing. In an additional control condition, participants learned foreign language words by viewing pictures, whose translation was unaffected by TMS applied to the motor cortex.
The results
The motor cortex contributed to the translation of foreign language vocabulary after a relatively brief period of gesture-based training, suggesting that performing gestures may be a valuable tool for picking up new words in a foreign language more quickly. “Interestingly, the effect occurred for both concrete words such as violin and abstract words such as democracy. Taken together, the findings suggest that our memory for recently-learned foreign language words depends on the sensorimotor context in which the words were experienced during learning,” explains first author Brian Mathias. “Many often-used teaching methods for learning new foreign language vocabulary rely on only audio or visual information, such as studying written word lists. Our findings shed light on why learning techniques that integrate the body’s motor system typically outperform these other learning strategies.”
Original Publication:
Brian Mathias, Andrea Waibel, Gesa Hartwigsen, Leona Sureth, Manuela Macedonia, Katja M. Mayer and Katharina von Kriegstein. Motor cortex causally contributes to vocabulary translation following sensorimotor-enriched training. Journal of Neuroscience 24 August 2021, JN-RM-2249-20; DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2249-20.2021
All latest news from the category: Studies and Analyses
innovations-report maintains a wealth of in-depth studies and analyses from a variety of subject areas including business and finance, medicine and pharmacology, ecology and the environment, energy, communications and media, transportation, work, family and leisure.
Newest articles

First-of-its-kind study uses remote sensing to monitor plastic debris in rivers and lakes
Remote sensing creates a cost-effective solution to monitoring plastic pollution. A first-of-its-kind study from researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities shows how remote sensing can help monitor and…

Laser-based artificial neuron mimics nerve cell functions at lightning speed
With a processing speed a billion times faster than nature, chip-based laser neuron could help advance AI tasks such as pattern recognition and sequence prediction. Researchers have developed a laser-based…

Optimising the processing of plastic waste
Just one look in the yellow bin reveals a colourful jumble of different types of plastic. However, the purer and more uniform plastic waste is, the easier it is to…



