New study provides a solution for engineering cellular materials
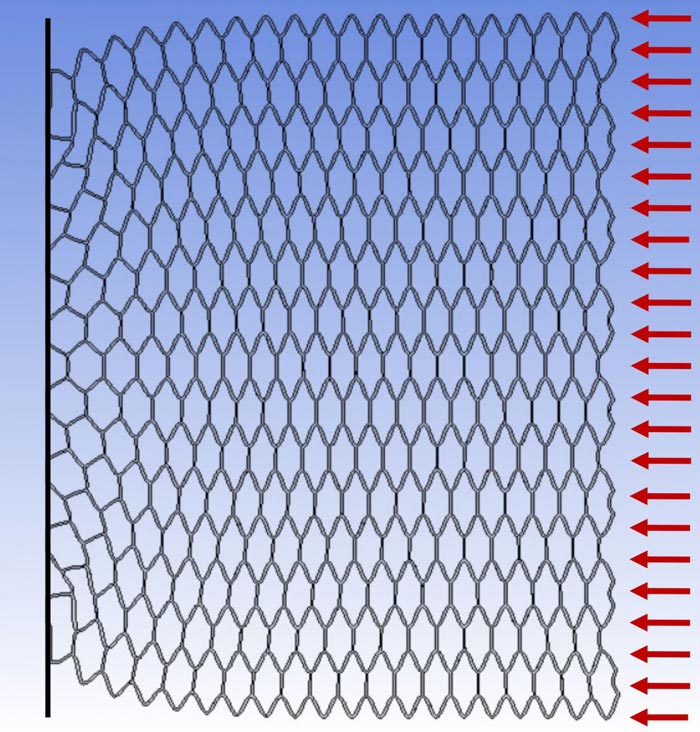
Lattice buckling: Hexagonal lattice under compressive force.
Credit: Micah Arago
A new study by a Swansea University academic has announced a new mathematical formula that will help engineers assess the point at which cellular materials, which are used a wide range of applications ranging from aerospace to the construction industry, will bend and buckle.
Professor Sondipon Adhikari, of the College of Engineering has published his findings in the Proceedings of the Royal Society A. The study details a formula that can calculate the elastic instability of cellular material, in this case hexagonal lattice material, also known as the honeycomb which is commonly used in the production of lightweight structures such as energy absorbent foams, mechanical and acoustic metamaterials and next-generation stent technology.
Professor Adhikari’s formula, which is a simple closed-form expression, will help engineers make quick design calculations and can also be used to benchmark future experimental and numerical studies.
Professor Adhikari said: “This paper is the result of two years of sustained research. The simple closed-form expression for critical buckling stress can be viewed as the extension of the classical Euler’s critical load formula, first derived in 1757 which calculated the stress point at which a beam will suddenly bend and buckle. This new expression is a 21st century solution for engineering cellular materials that will be used in advanced engineering applications now and in the future.”
All latest news from the category: Studies and Analyses
innovations-report maintains a wealth of in-depth studies and analyses from a variety of subject areas including business and finance, medicine and pharmacology, ecology and the environment, energy, communications and media, transportation, work, family and leisure.
Newest articles

Innovative 3D printed scaffolds offer new hope for bone healing
Researchers at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia have developed novel 3D printed PLA-CaP scaffolds that promote blood vessel formation, ensuring better healing and regeneration of bone tissue. Bone is…

The surprising role of gut infection in Alzheimer’s disease
ASU- and Banner Alzheimer’s Institute-led study implicates link between a common virus and the disease, which travels from the gut to the brain and may be a target for antiviral…

Molecular gardening: New enzymes discovered for protein modification pruning
How deubiquitinases USP53 and USP54 cleave long polyubiquitin chains and how the former is linked to liver disease in children. Deubiquitinases (DUBs) are enzymes used by cells to trim protein…



