innovations-report maintains a wealth of in-depth studies and analyses from a variety of subject areas including business and finance, medicine and pharmacology, ecology and the environment, energy, communications and media, transportation, work, family and leisure.
Study suggests damage is cumulative
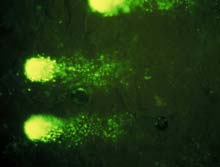
Prolonged exposure to low-level magnetic fields, similar to those emitted by such common household devices as blow dryers, electric blankets and razors, can damage brain cell DNA, according to researchers in the University of Washington’s Department of Bioengineering. The scientists further found that the damage from brief exposures appears to build up over time.
The new study is scheduled to be published in Environmental Health Perspecti

The effectiveness of the chickenpox vaccine decreases significantly in the first year after vaccination, and also appears lower if the vaccine is administered to children younger than 15 months of age, according to a study in the February 18 issue of The Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA).
According to background information in the article, chickenpox (varicella) vaccine is recommended for routine administration to healthy children at 12 to 18 months of age and to older chil

Danish researchers found that sun exposure behaviors and personal characteristics are correlated with the dose of ultraviolet radiation (UVR) a person receives, according to a report in the February issue of The Archives of Dermatology, one of the JAMA/Archives journals.
UVR exposure is a well-known risk factor for developing skin cancer, according to the article. Guidelines of safe limits of UVR exposure have been issued by many international health organizations. These limits are determin

Studies of natural antibiotics in our mouths may lead to new treatments for oral infections, as well as ways to boost the infection-fighting powers of mouthwashes, denture coatings, and wound dressings, according to a presentation at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS). These compounds, called beta-defensins, are key components of our innate immune system.
“Innate immunity describes the defenses that we’re are born with; they’re cod

There’s a big discrepancy between what science shows about recovered memories of childhood sexual abuse and what’s being shown in the media, according to University of Oregon memory researcher Jennifer Freyd.
Most people find recovered memories less believable than events someone has always remembered, despite research showing that whether a memory is true or not has no documented relationship to whether it was always remembered or only recently remembered, Freyd says.
U

Individuals with autism have been shown to have a difficult time recognizing faces, but two University of Washington researchers now suggest that the problem may be due to a lack of practice, rather than to abnormal functioning of the affected region of the brain.
Previous research, using an electroencephalogram (EEG) to measure brain activity, had shown that autistic 3- and 4-year-olds failed to show normal brain response when viewing their mother’s picture. However, a recent study re