
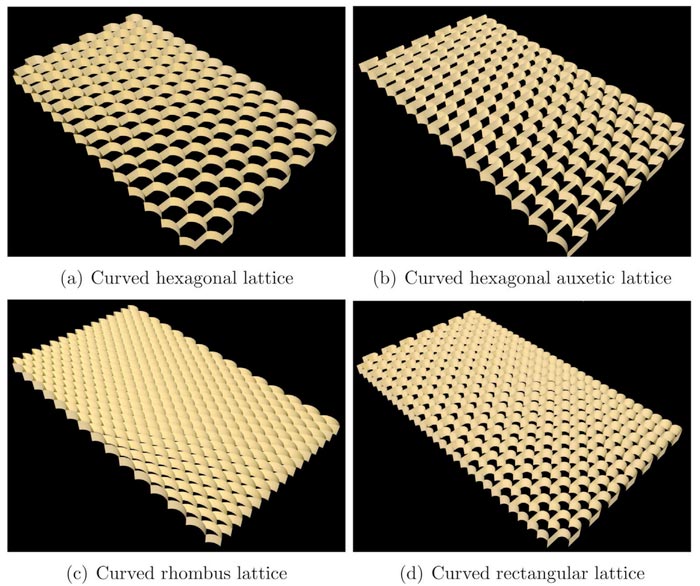
Family of curved 2D lattices conceived and analysed in the study (a) The curved hexagonal lattice, (b) The curved hexagonal auxetic lattice, (c) The curved rhombus lattice, and (d) The curved rectangular lattice.
Credit: S. Mukherjee
A new study from Swansea University has introduced a framework to calculate the material properties of a new class of two-dimensional curved hexagonal lattices that could be used in the production of improved mechanical metamaterials found in bio-engineering, stretchable electronics, impact absorption and soft robots.
The research published in the Composite Structures journal, outlines how the research team from the university’s Faculty of Science and Engineering pioneered the new framework of calculations, known as generalised closed-form expressions.
Dr Shuvajit Mukherjee who co-authored the study said: “This paper represents fundamental analytical approaches to obtain the most general closed-form expressions of the equivalent material properties of 2D hexagonal lattices. This work captures a large class of geometry. Introduction of the curved beam as constituent beam members of the unit cell of the lattice enrich the design space and enhance the flexibility of the structure.”
Co-author, Professor Sondipon Adhikari said: “The introduction of a curved beam element in the unit cell results in increasing the flexibility of the lattice and it also expands the design space for lattice materials. The closed-form expression can be utilised as a benchmark solution for future numerical and experimental investigations. It also can be exploited to obtain user-defined mechanical properties.”
Journal: Composite Structures
DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2021.114859
Article Title: The in-plane mechanics of a family of curved 2D lattices
Article Publication Date: 3-Nov-2021
Media Contact
Delyth Purchase
Swansea University
d.purchase@swansea.ac.uk














