
Mayor improvement for particle research at CERN Scientists working together in the “Antihydrogen Experiment: Gravity, Interferometry, Spectroscopy” (AEgIS) and other experiments at CERN’s Antimatter Factory, such ALPHA and GBAR, are on a mission to measure the free-fall of antihydrogen under Earth’s gravity with high precision, each using a different technique. AEgIS’s approach involves producing a horizontal beam of antihydrogen and measuring its vertical displacement using a device called a moiré deflectometer that reveals tiny deviations in motion and a detector…

From virtual reality to rehabilitation and communication, haptic technology has revolutionized the way humans interact with the digital world. While early haptic devices focused on single-sensory cues like vibration-based notifications, modern advancements have paved the way for multisensory haptic devices that integrate various forms of touch-based feedback, including vibration, skin stretch, pressure and temperature. Recently, a team of experts, including Rice University’s Marcia O’Malley and Daniel Preston, graduate student Joshua Fleck, alumni Zane Zook ’23 and Janelle Clark ’22 and other collaborators, published…

Plasmonic modulators are tiny components that convert electrical signals into optical signals in order to transport them through optical fibres. A modulator of this kind had never managed to transmit data with a frequency of over a terahertz (over a trillion oscillations per second). Now, researchers from the group led by Jürg Leuthold, Professor of Photonics and Communications at ETH Zurich, have succeeded in doing just that. Previous modulators could only convert frequencies up to 100 or 200 gigahertz – in…
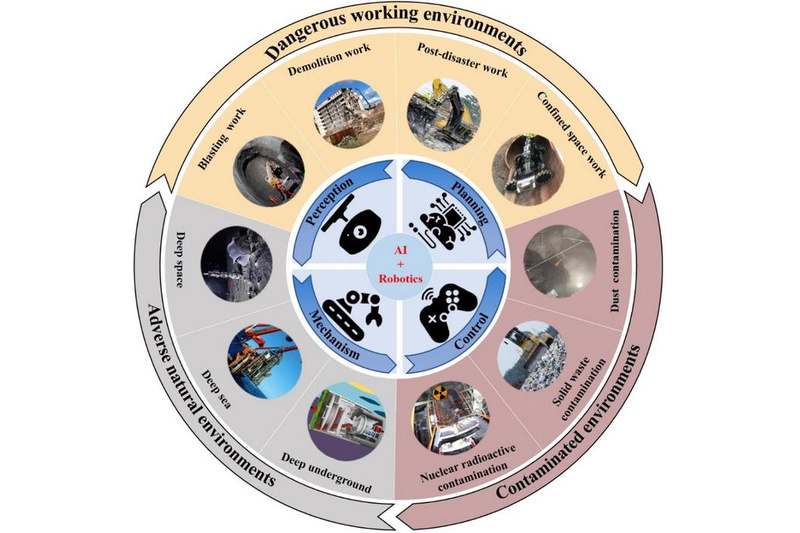
As the new wave of technological revolution and industrial transformation progresses, scientific research is expanding towards the macroscopic, delving into the microscopic, and advancing into extreme conditions, which becoming the developmental trends at the forefront of global science and technology. With the implementation of national strategies such as the high-quality development of green and low-carbon, China faces a series of new scientific and technological challenges in the field of construction under extreme environments. Among these, construction robotics in extreme environments,…

Researchers from Osaka University introduced an innovative technology to lower power consumption for modern memory devices. Stepping up the Memory Game: Overcoming the Limitations of Traditional RAM Osaka, Japan – Numerous memory types for computing devices have emerged in recent years, aiming to overcome the limitations imposed by traditional random access memory (RAM). Magnetoresistive RAM (MRAM) is one such memory type which offers several advantages over conventional RAM, including its non-volatility, high speed, increased storage capacity and enhanced endurance. Although…

Cutting-Edge Framework for Enhancing System Security Researchers at the University of Electro-Communications have developed a groundbreaking framework for improving system security by analyzing business process logs. This framework focuses on ensuring that role-based access control (RBAC) rules-critical to managing who can access specific system resources-are correctly implemented. Noncompliance with these rules, whether due to error or malicious activity, can result in unauthorized access and pose significant risks to organizations. Challenges in Ensuring Compliance with RBAC Policies RBAC is a widely…

The invention provides novel lithium salts of pentafluorophenylamide, in particular, lithium pentafluorophenyl (trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide (Li-PFTFSI). Li-PFTFSI has improved thermal stability and ion mobility compared to known lithium salts.
These characteristics make Li-PFTFSI desirable for use as electrolytes in lithium ion batteries.

The newly developed method aims at producing small gratings on different materials, especially on glass surfaces, by ablating small amounts of material. The gratings can be small enough to form patterns with a diffractive effect causing the material to schiller in different colors.

Immunization is an important tool to fight diseases caused by viral, bacterial or fungal pathogenes. The invention provides a new approach for the generation of oligomeric vaccines. The underlying principle is the high affinity interaction between S-protein and a modified S-tag of bovine pancreatic RNase A which is applied to hemagglutinin (H5). The technology can be applied to produce high molecular vaccines. They have many advantages compared to recently used vaccines including high immunogenicity, high stability, short production time and lower production costs. The approach could therefore be used for the immunization of livestock.

Traditional battery materials, e. g. for Li-ion batteries are brittle, thus not suitable for high capacity flexible batteries. Rigid organic redox polymer batteries have low volumetric energy and power density.
Using a new colloid consisting, of redox pol-ymer and graphene oxide that is trans-formed into reduced graphene oxide during preparation, thickness scalable cathodic and anodic battery materials reaching 1.3 mAh/cm2 for flexible and at least 21 mAh/cm2 for rigid materials are available. The new technologa offers the following advantages:
higher capacities materials for flexible batteries,
scalability 1 – 20 mAh/cm2,
tailord redox-potential and
non-toxic materials.

“Q-primers” are ammonium compounds, which make it possible to permanently functionalize virtually any surface. It is an environmentally friendly and cost-effective process that allows the production of ultra-thin layers and an “on demand” functionalization. The carrier quat primer can be equipped with any functional groups so that an universally applicable strategy for the modification of surfaces is now available.

This innovative carbonization process of carbon precursor fibers creates in a fast and energy saving manner carbon fibers (CF) which are highly porous (small pore diameters from 0.1 to 10 nm) and have a high surface area (100 to 2500 m2/g). The pyrolysis step needs only minutes or even seconds.
No additional additives like pore-providing templates, catalytic compounds or corrosive liquids are required. However, filler materials like pigments, dyes, graphene nanoplatelets or metal- and semiconductor nanoparticles can be admixed to vary the performance of the produced carbon fibers, e.g. to increase electrical conductivity. Overall, this technology combines conventional carbonization and activation treatments into one process and is more economical by saving time, costs and resources compared to already known thermal carbonization methods.
Applications of carbon fibers are known in the art. Electric applications like super caps and electrodes or filtration and adsorption for gas, water and solvent purification might be preferable.

A herbal remedy is effective against the Ebola virus. The natural compound silvestrol reduces the number of pathogens in infected cells. Also the production of virulent proteins is largely suppressed if the natural substance is used.

Yellow mosaic virus disease leads to substantial losses – up to 50 % of the yield – in susceptible barley varieties (Hordeum vulgare). The disease is caused by different strains of Barley yellow mosaic virus (BaYMV) and Barley mild mosaic virus (BaMMV). It cannot be cured by chemical treatment. The present invention provides a new recessive resistance gene. Variants of the gene lead to resistance against all agents known to cause yellow mosaic virus disease in Europe.

Parenteral controlled drug delivery is of crucial importance for the pharmacotherapy of many diseases (e.g. breast and prostate cancer, local inflammation). By means of controlled release systems it is possible to decrease the frequency of administration (from hours to months), to increase drug efficiency and to decrease side effects. The problem is solved by providing Direct Injectable Polymer Solutions (DIPOs) which act as a depot after administration. Their polarity and degradation rate is adjustable. They are much less acidic compared to PLA/PLGA polymers.

Parenteral controlled drug delivery is of crucial importance for the pharmacotherapy of many diseases (e.g. breast and prostate cancer, local inflammation). By means of controlled release systems it is possible to decrease the frequency of administration (from hours to months), to increase drug efficiency and to decrease side effects. Direct Injectable OleoGels (DIOGs) and In Situ Forming OleoGels (ISFOGs) were developed as new, biodegradable and lipid based formulations for parenteral controlled release applications. Both formulations have many advantages in terms of manufacturability, rheological properties and release control compared to the currently used drug delivery systems.