Rapid testing of food quality
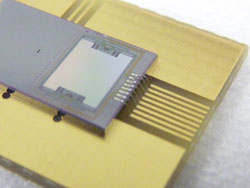
Complete with integrated diffraction grating, grating drive, position detector and optical gaps, the spectrometer is much more compact than those currently available in the market. © Fraunhofer IPMS<br>
Is that pear ripe? Or will you be annoyed when you get home and discover that the one you bought is neither sweet nor juicy? And what about that meat? Does it contain too much water, which will make it turn tough when you cook it?
Buying the right food is often a question of sheer luck for consumers. But all that is set to change. In future, all you will need to do is hold your smartphone near the product in question, activate the corresponding app, choose the food type from the menu – e.g. “pear” – and straight away the device will make a recommendation: the fructose content of the pear is high, so buy it!
The application is based on a near infrared spectrometer which measures the amount of water, sugar, starch, fat and protein present in the products. The system “looks” several centimeters below the outer surface of the foodstuffs – which means it can detect, for instance, whether the core of an apple is already rotting. Thin packaging film is no problem for the device as it takes measurements straight through it.
But how does the device actually work? By shining a broad-bandwidth light on the item to be tested – for instance a piece of meat. Depending on the meat’s composition, it will reflect different wavelengths of light in the near infrared range with different intensities. The resulting spectrum tells scientists what amounts of which substances are present in the foodstuff.
Smaller than a sugar cube
The novel thing about this spectrometer is its size. With a volume of only 2.1 cc, it is 30 percent smaller than a sugar cube, and thus substantially more compact than its commercially available counterparts, which are around 350 times larger. Another advantage is that the devices are inexpensive to make and suitable for mass production. “We expect spectrometers to develop in the same way that digital cameras did,” says Dr. Heinrich Grüger, who manages the relevant business unit at the Fraunhofer Institute for Photonic Microsystems IPMS in Dresden, where the system is being developed. “A camera that cost 500 euros ten years ago is far less capable than the ones you get virtually for free today in your cell phone.”
Spectrometers are usually manufactured by assembling individual components: The mirrors, optical gaps, grating and detector each have to be put in place individually and properly aligned. The IMPS researchers instead manufacture the individual gratings and optical gaps directly on silicon wafers. But that’s not all: The thin silicon wafers are large enough to hold the components of several hundred spectrometers, which means that hundreds of near infrared systems can be produced in one go. The scientists stack the wafers containing the integrated components on top of the ones bearing the optical components. They then align and bind the wafers, and isolate them to form individual spectrometers. This means the researchers do not need to position each component, but only the respective composite substrates. Another advantage of what is called Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS) technology is that the devices produced are much more robust than their handmade counterparts.
At the Sensor+Test tradeshow being held in Nuremberg from May 22 to 24, the IPMS research scientists will be exhibiting a prototype of the spectrometer (in Hall 12, Booth 202). The device could be ready for market launch in three to five years. The researchers are also working on creating a corresponding infrastructure. “We are developing intelligent algorithms that analyze the recorded spectrums immediately, compare them with the requirements and then advise the consumer whether or not to buy the item. This advice is based solely on quality features such as ripeness and water content. The system cannot carry out a microbiological or toxicological analysis.” Potential application areas for the spectrometers are not limited to foodstuffs: The device can also detect forgeries, for example, and can verify whether a product is made of high-quality original materials or whether it is a cheap fake. It can also reveal whether parts of a vehicle’s body have been repainted, as well as test the contents of drugs and cosmetic creams.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Trade Fair News
Newest articles

Self-Destructing Cancer Cells: Cutting-Edge RNA Breakthrough
Jülich scientists use novel RNA technology to selectively switch off tumours in the brain. An Adaptable Platform Technology That Destroys Glioblastoma Cancer Cells Using a special RNA molecule, a team…

Endurance Training: Transforming Lives of Heart Failure Patients
Can strength and endurance training be beneficial for patients with a certain form of heart failure? A research team from Greifswald investigated this question together with seven other research centers…

A Wake-Up Call for Mediterranean Shark Protection Against Extinction
Overfishing, illegal fishing and increasing marketing of shark meat pose significant threats to the more than 80 species of sharks and rays that inhabit the Mediterranean Sea, according to a…



